SEO Basics: A Beginner’s Guide to SEO Success for Businesses
This is a high-level guide on SEO basics for startups, small businesses, and entrepreneurs.
If you wish to learn:
- What SEO is all about
- Whether it’s worth your effort
- How SEO Works
- How to build an SEO-friendly website today
Then, you’ll love the strong foundation of SEO concepts covered in this guide. After covering the basics, you will learn the step-by-step process involved in the creation of an SEO-friendly website.
So, let’s dive in.

Why SEO? Why is SEO Important?
This is why!
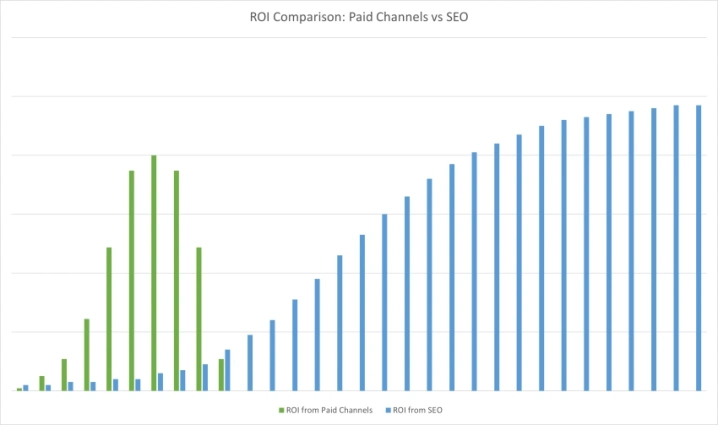
What makes SEO worth your time and money is that it delivers sustained results for a fraction of the cost of paid marketing.
Paid marketing, including google ads, TV ads, sponsored content, and influencer marketing, gives you immediate but limited results. The day your ad campaign stops, the impact tapers out and dies. This does not happen with SEO.
With Search Engine Optimization, you continue to remain relevant and top of mind for your audience in the long term. Even when you’re not actively reaching out to your audiences, they’ll continue to interact with your business and build a meaningful relationship with you organically through search engines.
There are also other benefits, such as brand authority, credibility, trust, greater reach, and a sustainable business model, among others, that make SEO an indispensable element of digital marketing strategy for businesses of all sizes.
What is SEO?
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of making your website more useful, more relevant, and easier for your audience to find on search engines like Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo, Yandex, Baidu, and others.
It encompasses everything you do to help your website rank higher in search results when your audiences are searching for something related to you or your industry.
Why SEO Basics?
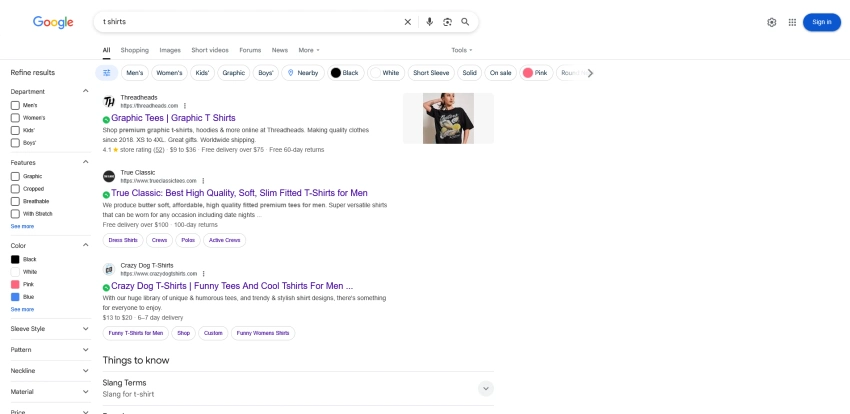
The simple answer is that SEO fundamentals are shifting beneath your feet. Take a look at this Google search results page for a product query. It looks like an eCommerce website with multiple filters.
Even general research searches look very different from a few years ago. As you can see below, the above-the-fold area is dominated by incumbent players, forums, news media sites, and so on. How do you breach them?
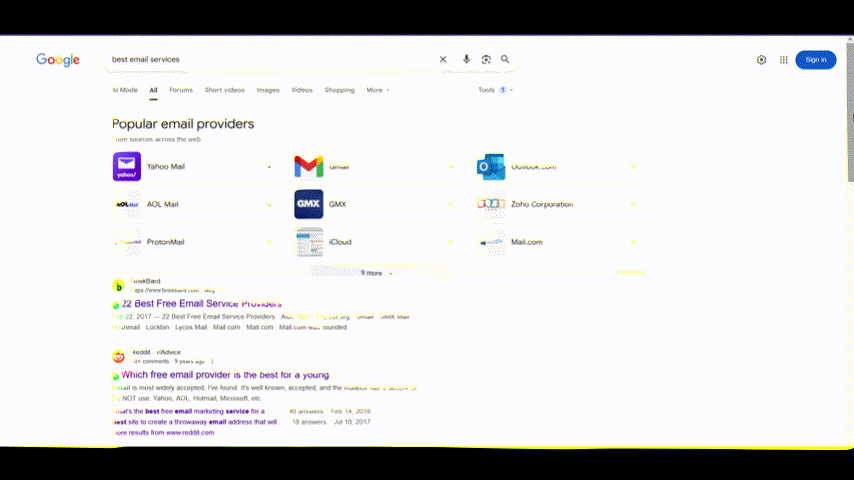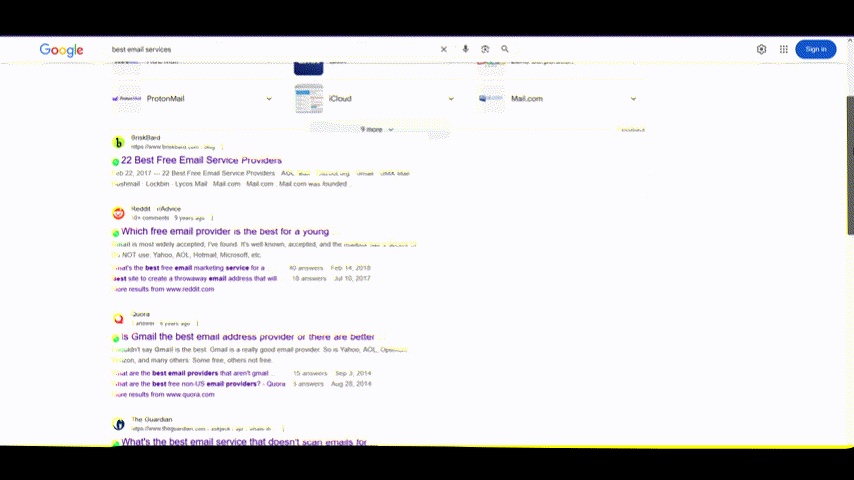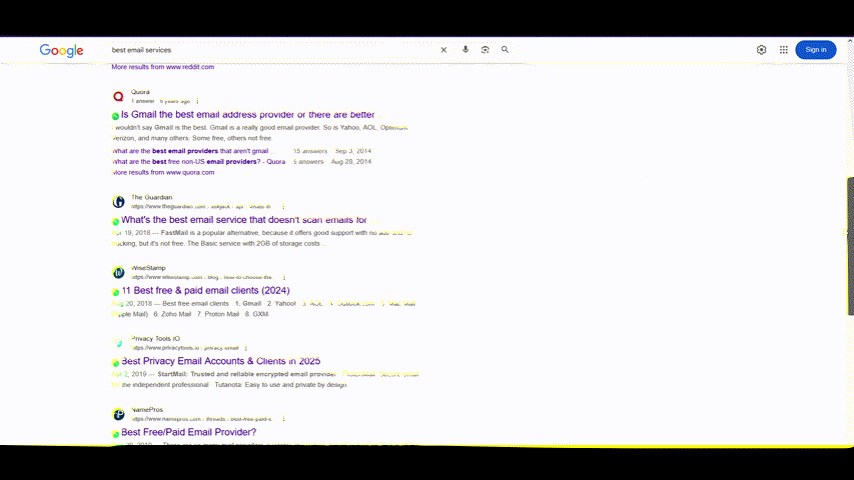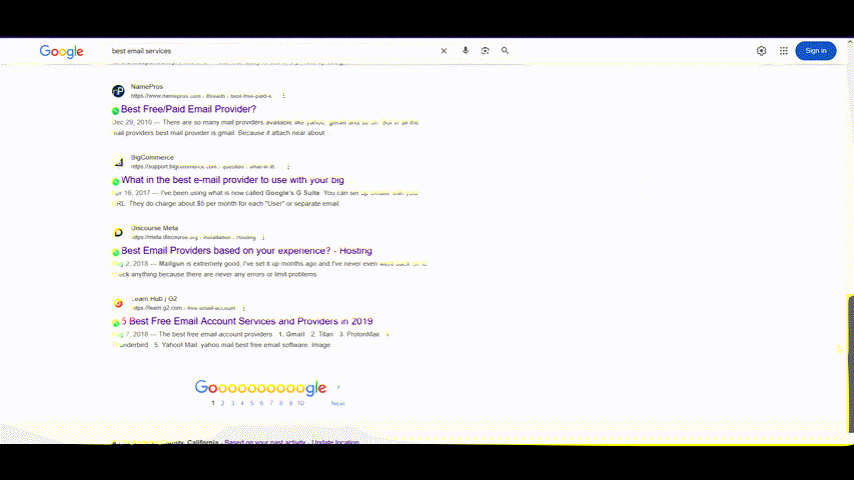
What worked a few years ago does not work anymore – at least not as effectively as it did before. Google algorithm is changing rapidly. So, it’s time to revisit the board, and that’s what we’re doing today.
Algorithmic updates to search engines, combined with the emergence of large language models (LLMs) and generative pre-trained transformers (GPTs), have introduced a significant shift in how users search and find answers to their questions. Consequently, businesses and webmasters must adjust their SEO strategies to accommodate these global shifts.
So, let’s get started, shall we?
Learn SEO Basics for Online Success
Search engine optimization can be broadly divided into 5 areas. You master these, and you can turn your website into an internet sensation.
Keywords Research
The first step is to find out the exact words, terms, and phrases your audiences use to look for answers on search engines. For instance, if you’re an online store selling baby shoes, your audiences could be using keywords like ‘baby shoes,’ ‘pink baby shoes,’ ‘toddler shoes’, ‘baby shoes 0-3 months,’ etc.
Thankfully, you don’t have to guess these keywords. A vast variety of keyword research tools, such as WordStream, Google Keyword Planner, and so on, will help you discover relevant keywords without any effort on your part.
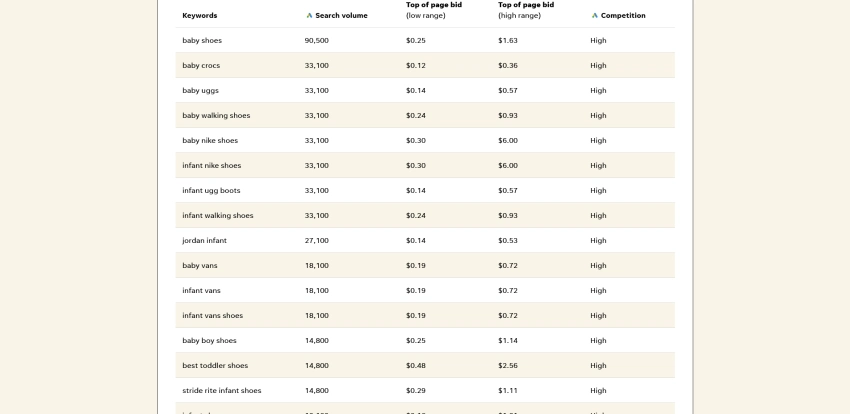
Check out this in-depth post on keyword research for SEO for detailed, step-by-step instructions on how to do it.
Content Creation
Once you identify the keywords your audience is using, you create blogs, videos, landing pages, and other types of content on your website that focus on those keywords. If your content aligns with the needs and intents of searchers, search engines will increasingly present it to your target audience, thereby increasing your visibility and popularity.
In fact, modern businesses rely on content marketing services to fuel their inbound marketing strategies.
On-page SEO
It’s not enough that your content is useful. It should be easy to read, understand, and digest for both humans and search engines. It should be structured and formatted in a way that makes it easy for search engines to understand. When done properly, on-page SEO ensures that search engines rank your content accurately and precisely, thereby boosting your ranking.
Off-page SEO or Link-building
At its heart, off-page SEO is all about building authority and trust from other websites that have already established their credibility. It’s like networking. The more reputable your referring websites are, and the more such websites link to you, the more authority your website gains in the eyes of search engines.

Technical SEO
With technical SEO, you address issues on your website that prevent or hinder search engines from crawling, indexing, and ranking your content. The easier it is for search engines to find and index your content, the better your chances of ranking high in search results.
How To Do SEO For Website: Step-by-step Guide
This is a crash course on website SEO for beginners. It covers the most basic aspects of website SEO that you can implement today to create an SEO-friendly website.
Step 1: Choose a Good Domain Name
From an SEO perspective, your domain name is one of the most powerful and important signals for search engines. It should be clear, sharp, and descriptive, yet as concise as possible. Ideally, no hyphens or special characters should be used.
Something simple, like DONSDINER.COM, is a lot more effective than something fancy, like DONZZZ.COM.
If someone can guess what you or your business is all about just by looking at your domain name, then you’ve found the right one.
Step 2: Top-level domain (TLD)
A top-level domain (TLD), also known as a domain extension, refers to the part after the dot in a domain name. It could be .COM, .NET, .BIZ, or one of several others. For SEO purposes, the choice of TLD is not particularly significant.
That said, it does matter to internet users. COM is the most familiar and trusted domain extension. So, .COM domain is usually the right option.
In some cases, however, other domain extensions would be more suitable. For instance, an educational institution may benefit from using .EDU domain extension. If you’re a local or national business with no international presence, country-specific domain extensions like .CO.UK, .CO.AU, etc. may be the right choice.
Step 3: Choose an Appropriate Content Management System
It’s time to make some crucial decisions on the tech stack on which your website will be built. If you have the technical background or a team to do it, you can create a custom website from scratch – front end, back end, and everything in between. Otherwise, it’s best to use a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, Wix, Shopify, Joomla, and the like.
Your choice of CMS should be based on your expertise, familiarity, convenience, budget, business needs, and other relevant factors. Shopify works best for online stores. Wix makes web building simple and easy. WordPress is ideal for webmasters who desire more customization options.
Step 4: Choose the Right Website Hosting Provider
A hosting provider is where your website will be hosted. They provide the server resources to keep your website live and active 24/7.
The hosting service you choose should be located in or close to your audience’s location. It doesn’t matter if you are operating out of another country like UK, Germany, or Japan. If your audience is in the US, for instance, your hosting provider should ideally be located in the US.
Of course, they should also have an excellent website uptime record and a proven history of reliability.
Generally, website hosting providers offer multiple hosting services, including Shared Hosting, Virtual Private Servers (VPS), and Dedicated Hosting, among others. Select one that best suits your unique needs.
Step 5: Create a User-friendly and Intuitive Website Structure
Your website must be easy to navigate for both human users and search engine bots. The more user-friendly, intuitive, and well-structured your website is, the easier it will be for users and bots to find relevant content on your website. An intuitive website structure is good for both on-page and technical SEO.
Here are some things you can do to create an intuitive, easy-to-navigate website:
- All pages must have a clear and consistent layout
- Navigation Menu should be simplified, and all pages must be organized for intuitive access. Service pages must be listed under the Services menu item, industry pages under the Industry menu item, and so on.
- The entire website must have a responsive, mobile-friendly design
- Every webpage must be optimized for fast-loading
- Lazy-load images and use advanced image compression
- Use clear calls to action (CTAs) to tell visitors what to do next, no matter where they are on the website
- Create user-friendly content in simple language. Avoid jargon as much as possible.
Here’s what a good website structure for a product business website or an online store would look like.
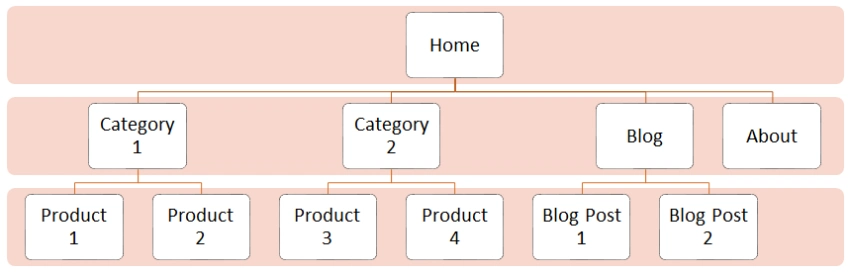
And, here’s what a good website structure for a service business website would look like.
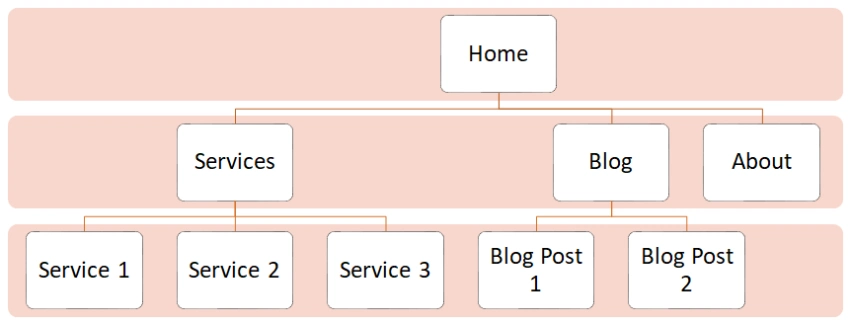
Step 6: Use an Intuitive and SEO-friendly URL Structure
Note: If your website is already live and has numerous pages, it’s not advisable to modify the URL structure. It can cause a number of technical issues and may even break several of your web pages.
However, if you’re building a new website, ensure that you follow a hierarchical URL structure. For an online children’s products retailer, a product URL may look something like this:
www.example.com/shoes/toddler-shoes-0-3-months/
A blog post on the same website may look something like this:
www.example.com/blog/best-toddler-shoes/
However, this hierarchical structure isn’t the only way to design your URLs. WordPress offers 5 presets in total:
- Plain: example.com/?p=75
- Day and name: example.com/2025/02/08/best-toddler-shoes/
- Month and name: example.com/08/07/best-toddler-shoes/
- Numeric: example.com/56/
- Post name: example.com/best-toddler-shoes/
WordPress also allows you to customize the URL structure if you’re not satisfied with any of the presets. You can use it to devise a more intuitive structure that best suits your needs.
Cannot make up your mind? Check what your competitors are doing and replicate it. This usually works for most businesses.
Step 7: Install SEO Plugins
Your website can tremendously benefit from a vast variety of website plugins. However, every new plugin you install on your website makes it a tad bit heavier and slower, which becomes a whole another problem to solve. Suffice it to say that your website must load quickly – typically within 2-4 seconds.
So, only install the most essential plugins.
For starters, the following plugins are essential for WordPress SEO:
- Yoast: For on-page and technical SEO.
- Site Kit by Google: Integrates with Google Analytics and Google Search Console
Step 8: Ask Google and Bing to Index Your Website
You’ve created a website, published content, and you’re finally live. But, search engines like Google and Bing do not know that. So, they cannot crawl, index, and rank your web pages just yet.
They will eventually discover your website through backlinks created on other websites, such as business directories or industry-specific websites. However, you can speed up this process by directly requesting search engines to index your website.
You should know 3 things to create indexing requests with search engines:
Search Engine Indexing Tools
Log in to Google Search Console (GSC) and send a website indexing request to Google search engine by submitting the XML sitemap. Check out this video for step-by-step instructions on how to submit your website sitemap to Google Search Console
To do the same for Bing search engine, you can use Bing Webmaster Tools and follow the instructions in this video below.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap contains your website’s complete structure, including URLs to individual pages and blog posts. This helps search engines easily discover, crawl, index, and rank all your pages. It’s usually located at one of the following locations:
example.com/sitemap.xml
example.com/sitemap_index.xml
Robots.txt file
This is a text file that instructs search engines on which pages to index and which to exclude. However, please note that the instructions in this file are merely suggestions, not rules. Search engine crawlers can ignore the instructions altogether and index all public pages on your website. It’s usually located at this location:
example.com/robots.txt
Step 9: Learn Advanced SEO to Boost Your Website Ranking
This guide on SEO Basics offers you the solid foundation you need to begin your SEO journey with confidence. Going forward, we’ll be covering more advanced SEO techniques, strategies, and tips. Stay tuned to beef up your SEO skills and unlock sustainable growth.
You can also complement your SEO knowledge with external resources such as:
- LearningSEO.io
- Google Skillshop
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Specialization by UC Davis on Coursera
Final Thoughts
That wraps up this SEO basics guide.
Do you feel that you benefited from this guide?
Do you have a question you’d like me to answer?
Did you find something missing, and would like me to cover it?
I’d love to hear your thoughts. Drop a comment below.
If you’d like to know more about how we do SEO, check out our Search Engine Optimization Services, or get in touch.

Leave a Reply